Language configuration
This page describes how language is configured in Magnolia.
Setting an editor’s language preference
To set a user’s language preference:
-
Open the Security app (Apps > Security).
Type securityin the Find Bar. -
Select the user profile you wish to edit.
-
Click Edit user.
-
Select a language from the Language dropdown.
| When the user signs in the next time, the UI is displayed in their preferred language. |
Available system languages
System languages are configured in Configuration >
/server/i18n/system. Each locale has language and country
properties that define the locale when combined. This allows you to
define regional variations such as zh-TW for traditional Chinese or
pt-BR for Brazilian Portuguese.
server:
i18n:
system:
fallbackLanguage: en
languages:
en:
country:
enabled: true
language: en
pt:
country:
enabled: true
language: pt
pt_BR:
country: BR
enabled: true
language: pt
zh_CN:
country: CN
enabled: true
language: zh
zh_TW:
country: TW
enabled: true
language: zh
Enabling multilanguage content
To enable multilanguage content:
-
Enable multilanguage authoring.
-
Set
i18n=true:-
In form fields.
-
On content type properties.
-
-
Define locales for the site.
Enable multilanguage authoring in /server/i18n/authoring. This allows editors to enter the same content in multiple languages.
server:
i18n:
authoring:
class: info.magnolia.multisite.i18n.MultiSiteI18nAuthoringSupport
enabled: true
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
|
required, default is Enables multilanguage content entry. |
|
required A class that implements info.magnolia.ui.api.i18n.I18NAuthoringSupport such as:
|
Set i18n=true
In form fields
Set the i18n property to true in all
fields where you
want to enter multilanguage content.
Example: Multilanguage content is enabled for the title text field.
form:
properties:
title:
$type: textField
i18n: trueOn content type properties
Add the i18n property with the true value to all content type model properties where you want to enter multilanguage content.
Example: The text field description is enabled for multilanguage content entry.
datasource:
workspace: tourvehicles
rootPath: /
autoCreate: true
model:
properties:
- name: description
i18n: trueDefine locales for the site
Define the languages that editors should be able to choose as locales in
the site definition under
<site>/i18n/locales.
Example: en, de and cs locales in an example test site definition.
test:
i18n:
enabled: true
class: info.magnolia.cms.i18n.DefaultI18nContentSupport
fallbackLocale: en
defaultLocale: cs
locales:
cz:
country: CZ
language: cs
enabled: true
de:
country: DE
language: de
enabled: trueProperties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
|
optional, default is Enables support for localized content. Used to rewrite URIs and getting nodes based on the current language. |
|
required Class that implements info.magnolia.cms.i18n.I18nContentSupport such as:
|
|
optional, default is Content is served for the fallback locale if content is not available for the current locale. |
|
optional If no locale can be determined, the default locale will be set. If no default locale is defined, the fallback locale is used. |
|
required |
|
required Locale ID that consists of language and country such as |
|
optional Country code such as |
|
required Language code such as |
|
optional, default is Enables the locale. |
|
Configure locales for the fallback site
If i18n is enabled in the configuration of your content app, you need to configure locales for the fallback site or extend a site definition with locales. Then, when editing structured content, the locales of the fallback site will be used while showing the language dropdown. |
Once multilanguage content entry is enabled, the page editor displays a language dropdown.
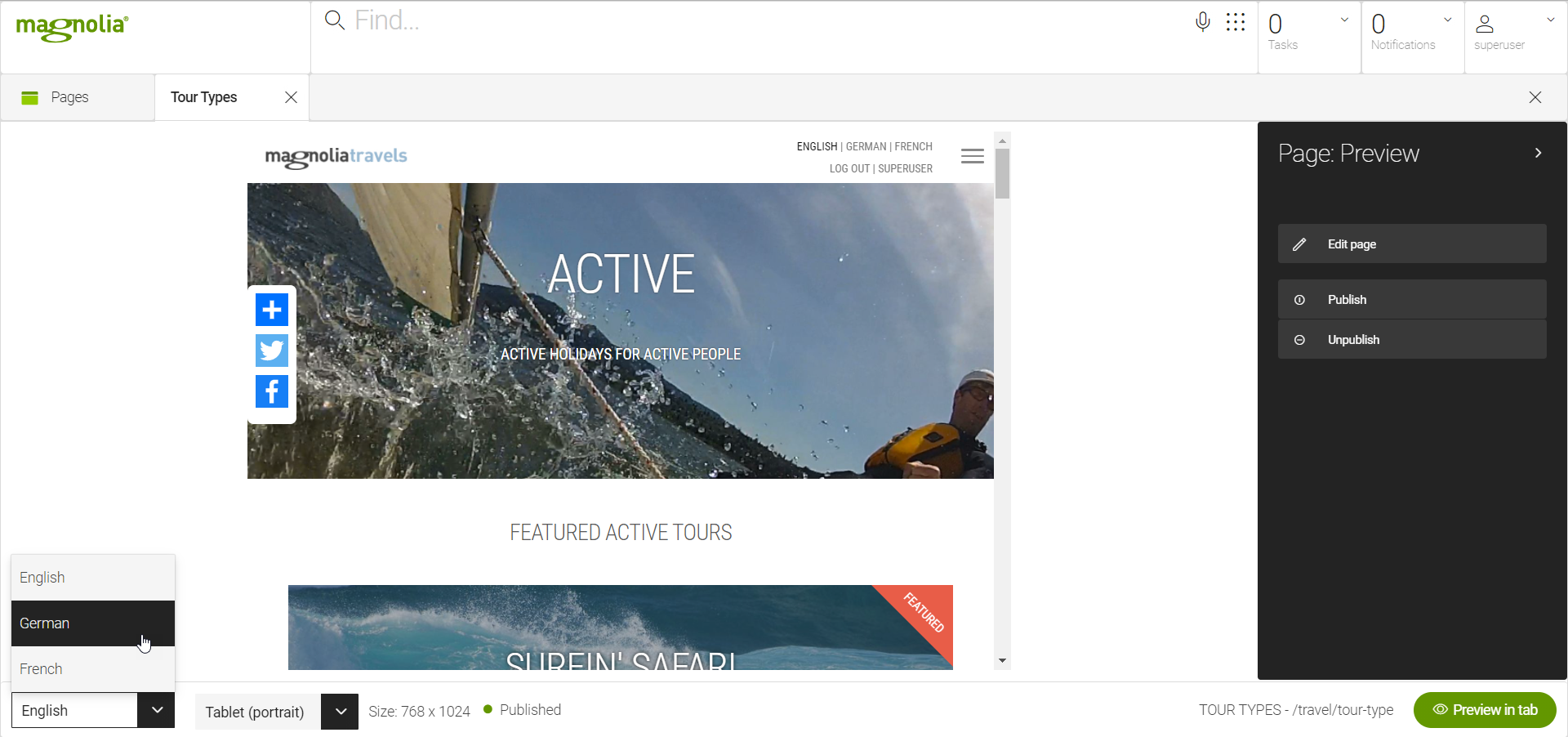
When you select a language from the dropdown, dialogs show a language
identifier such as fr next to field labels. This makes it clear what
language editors should be entering.
The language identifier is not displayed for the fallback locale, unless
the
i18n property is set to true in the definition of the given dialog.
For example, if your fallback locale is English you won’t see (en) next
to the field label.
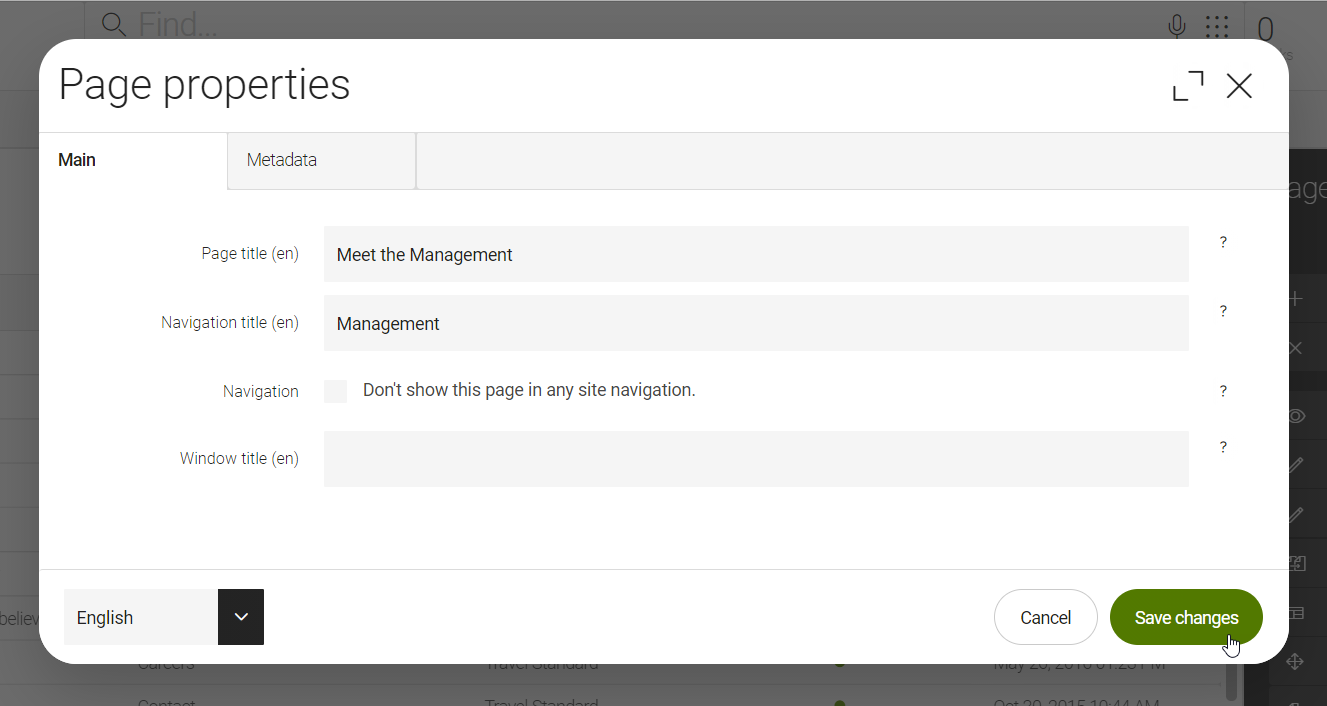
Displaying the locale dropdown and a locale identifier in the dialog is Magnolia’s default way to let editors choose a language. You can implement your own alternative such as separate tabs for each language. If the number of supported languages is not very large, the tab approach works well. The default approach works with any number of languages while keeping UI changes minimal.
|
The Content Translation Support module allows you to export and re-import page content in translation-friendly CSV and Excel formats. |
Storing and serving localized content
Magnolia stores translated content in the repository and serves it at a
language-specific URL such as mysite.com/de/welcome.html. Language
variations are stored in a single content hierarchy. You have the option
to disable the localized content storage and create a separate site
hierarchy for each locale instead.
Enable i18n content support in /server/i18n/content.
server:
i18n:
system:
content:
enabled: true
class: info.magnolia.module.site.i18n.SiteI18nContentSupport
authoring:| Property | Description |
|---|---|
|
required, default is Enables multilanguage content storage and delivery. |
|
required Class that implements info.magnolia.cms.i18n.I18nContentSupport such as:
|
One hierarchy or many
Magnolia can store multilanguage content in a single JCR content node. This means you only need one site hierarchy even if you serve content in many languages. However, there are cases when you may want to create language specific sites. See: Multilanguage structure.
If you go with the default one-hierarchy strategy, translations are
stored as separate properties under a single content node. In the
example below, a Text and Image component is translated into English,
German and French. The system creates subtitle and text properties
for each language under the 01 component node. Each property is
suffixed with a language identifier: _de or _fr. Since English is
the default locale (defaultLocale) on this site, no _en suffix is used.
content:
00:
01:
imageLocation: left
subtitle: Translation
subtitle_de: Übersetzung
subtitle_fr: Traduction
text: <p>Translation of the user interface text is a community-supported project.</p>
text_de: <p>Übersetzung der Benutzeroberfläche Text ist eine Gemeinde unterstützt das Projekt.</p>
text_fr: <p>Traduction du texte de l'interface utilisateur est un projet soutenu de la communauté.</p>Language-specific URL
Localized content is served to visitors at a URL that identifies the locale:
| Locale | URL |
|---|---|
Default locale |
|
German |
|
French |
|
Spanish |
|
Correspondingly, the HTML element on the public page identifies the
language with standard lang and xml:lang attributes.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xml:lang="en" lang="en" class="no-js">Magnolia does not redirect visitors to the localized URL automatically. You need to configure this behavior on the Web server. There are various strategies how you might want to do this but these are not provided out-of-the-box:
-
Allow the visitor to select a language or region from a dropdown, then redirect them to the correct URL. This is a common strategy on airline websites. Airlines serve customers in many countries and languages and allow users to select their home country regardless of where in the world they happen to be.
-
Detect the visitor’s origin from their IP or the referring page, then redirect them to the localized site.
-
Detect the visitor’s preferred locale from their browser settings, then redirect them to the localized site.
UTF-8 page names
Magnolia supports UTF-8 character encoding for Unicode. UTF-8 is able to represent any character in the Unicode standard and is backwards compatible with ASCII.
To enable UTF-8 character encoding in page names:
-
For JBoss AS, add the following section in
standalone.xmlordomain.xmlright after theextensionssection.standalone.xml or domain.xml<system-properties> <property name="org.apache.catalina.connector.URI_ENCODING" value="UTF-8"/> <property name="org.apache.catalina.connector.USE_BODY_ENCODING_FOR_QUERY_STRING" value="true"/> </system-properties> -
Enable Unicode support for content node and page names. Set the
magnolia.utf8.enabledproperty in amagnolia.propertiesfile.magnolia.properties# Activate UTF-8 support to pages magnolia.utf8.enabled=true (1)1 This allows you to use a variety of non-ASCII characters in node names. The value must be the same on both the author and public instance. Publication between instances with a different UTF-8 setting is not supported.
Sites built using Magnolia Templating Essentials templates identify the encoding as UTF-8 with an HTML meta element.
<meta charset="utf-8">